What is Monetary Policy?
Monetary policy is an economic policy controlled by central banks to manage the size and growth rate of the money supply within an economy. It is a powerful tool used to regulate macroeconomic variables such as inflation, unemployment, and currency exchange rates.
The money supply includes various forms of money, such as cash, checks, money-market mutual funds, and credit (loans, bonds, and mortgages). To manage the money supply, central banks increase or decrease liquidity. When a central bank increases liquidity, it aims to stimulate economic growth. Conversely, by reducing liquidity, it seeks to prevent inflation. Other factors beyond inflation are also affected, which influences the broader economy and helps the bank perform various regulatory tasks.
To achieve these objectives, central banks primarily use interest rates, reserve requirements, and open market operations involving government bonds.
Objectives of Monetary Policy
There are three main objectives of monetary policy: managing inflation, reducing unemployment (though central banks often prioritize inflation management before addressing unemployment), and maintaining stable currency exchange rates.
- Inflation: Typically, an inflation rate of around 2-3% is considered healthy for an economy. The Federal Reserve (The Fed), for example, has been largely successful in maintaining stable inflation rates over recent decades, even during global financial crises. When a central bank observes low interest rates and high consumer spending, it sees economic growth. However, to prevent the economy from overheating and facing high inflation, the bank may implement a contractionary monetary policy to reduce the money supply.
- Unemployment: When a central bank reduces interest rates, commercial banks offer more affordable loans to businesses, entrepreneurs, and individuals. As businesses expand, they create jobs and increase employment. However, because every economy has a limited number of resources and labor, central banks must maintain efficiency. If they perceive an inefficient use of capital or rising inflation, they may reduce the money supply, which can unfortunately lead to an increase in unemployment as a trade-off.
- Currency Exchange Rates: Monetary policy also plays a vital role in international trade. When a central bank observes that high liquidity is causing the domestic currency’s value to decrease relative to foreign currencies, it may reduce the money supply. By issuing less currency or tightening liquidity, the bank can stabilize or increase the value of the domestic currency. Conversely, increasing the money supply often leads to a depreciation in currency exchange rates.
Types of Monetary Policy
There are two primary types of monetary policy, which vary depending on the economic objective:
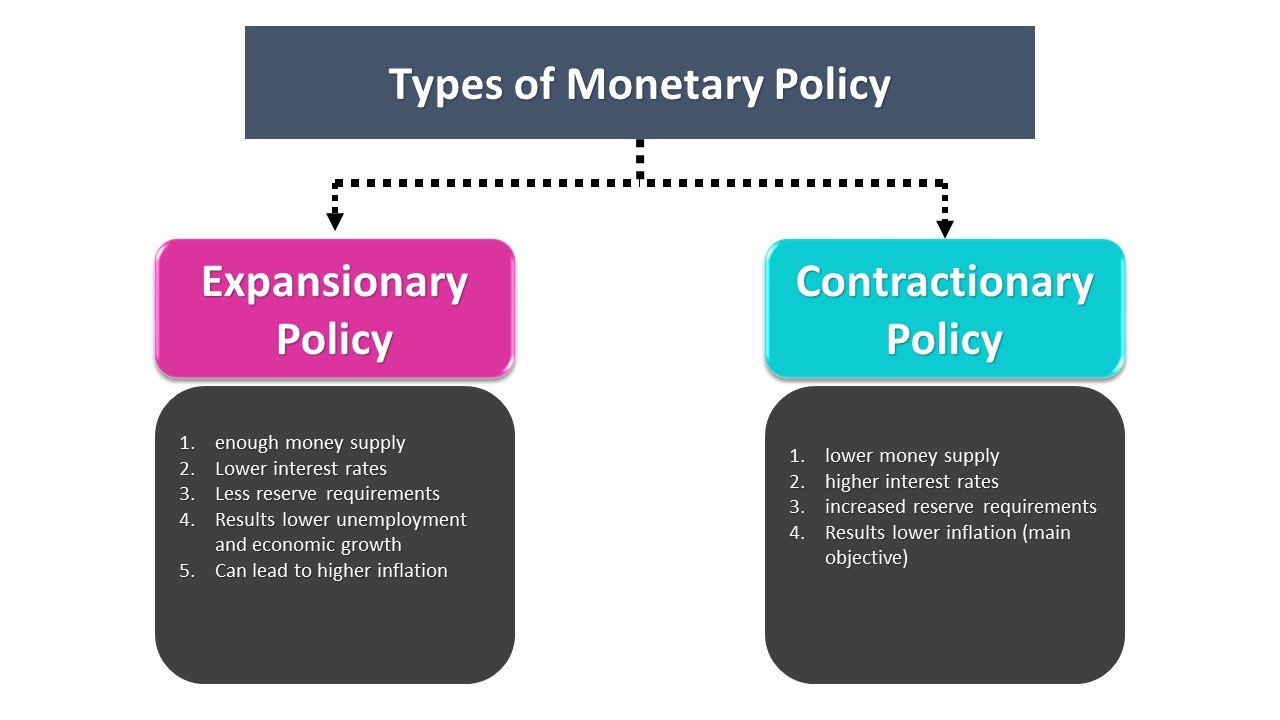
- Expansionary Monetary Policy: This policy aims to stimulate economic growth. It is implemented by decreasing interest rates, purchasing government securities, and lowering cash reserve requirements for commercial banks. With a higher money supply and lower interest rates, businesses and individuals are encouraged to take loans for expansion and consumption. This results in increased demand for goods and services, which ultimately creates jobs.
- Contractionary Monetary Policy: This is the opposite of expansionary policy. Its main objective is to reduce the money supply to prevent high inflation, correct inefficient uses of capital, and protect the value of the domestic currency. This is achieved by raising interest rates, increasing cash reserve requirements, and selling government bonds to remove liquidity from the system.
Tools of Monetary Policy
- Open Market Operations (OMO): OMOs are a primary tool used by central banks to buy and sell government bonds and other securities. To increase the money supply, central banks buy bonds from commercial banks, providing them with more cash to lend at lower rates. To decrease the money supply, central banks sell bonds, effectively taking cash out of the banking system, which reduces lending power and raises interest rates.
- Changing Reserve Requirements: The central bank sets the minimum amount of reserves a commercial bank must hold. If the central bank increases reserve requirements, commercial banks have less money available to lend, which supports a contractionary policy. If the reserve requirement is reduced, banks can lend more freely, increasing the money supply and encouraging expansion.
- Discount Rate Adjustments: The discount rate is the interest rate at which a central bank provides short-term loans to commercial banks. By manipulating this rate, the central bank influences overall interest rates. If the discount rate increases, commercial banks raise their own interest rates to maintain profit margins, slowing the economy. If the central bank wants to boost the money supply, it reduces the discount rate.
Powered by Froala Editor



