What is Unsupervised Machine Learning?
Unsupervised learning is a type of Machine Learning used to identify hidden patterns within data. It is often employed when you have a limited understanding of the dataset and want to explore inherent similarities. Unlike Supervised Learning, Unsupervised Learning does not rely on predefined features or labeled datasets, and it does not produce direct predictions or trained models in the traditional sense.
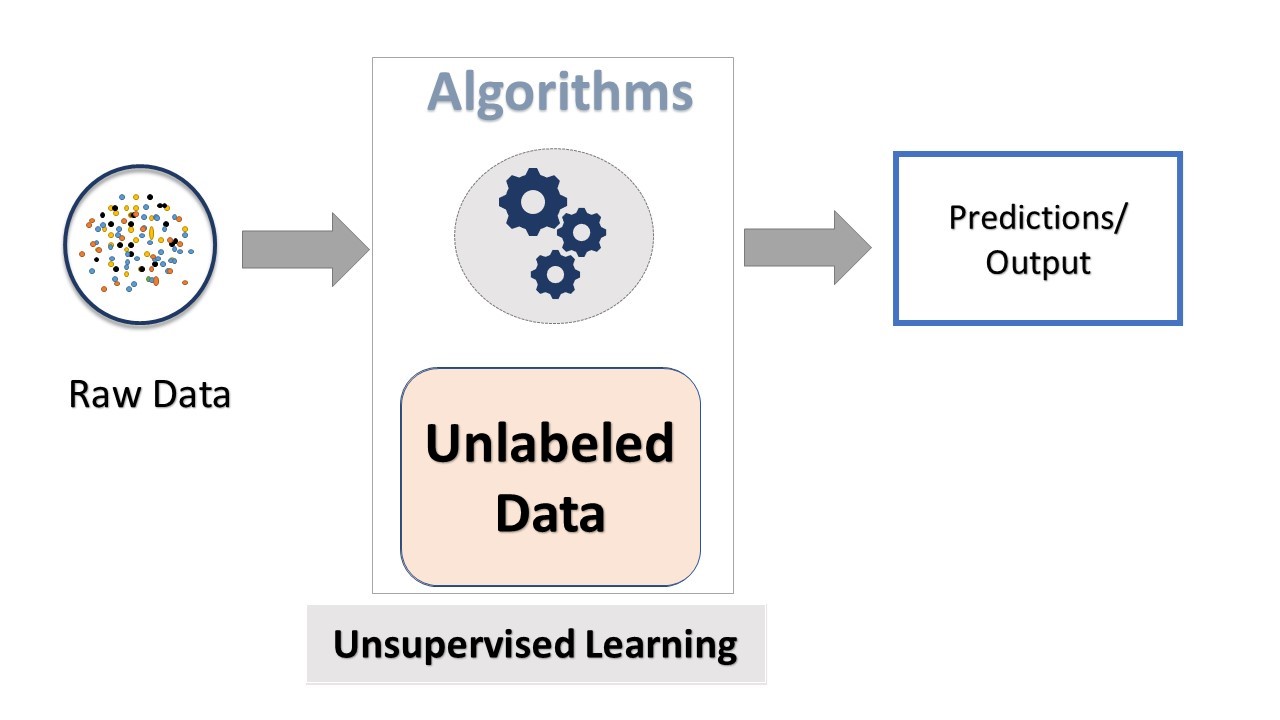 Unsupervised Machine Learning Working
Unsupervised Machine Learning Working
At the initial stage, Unsupervised Learning identifies features independently to generate outputs or group data. It is widely used in big data visualization and to build recommendation systems for platforms like YouTube, Netflix, and other OTT services.
Working of Unsupervised Learning
Unlike supervised machine learning, Unsupervised Learning does not use pre-labeled data. Instead, it processes unlabeled input data that has not been categorized based on specific attributes and lacks corresponding outputs for guidance. This unlabeled data is fed into the machine learning model to facilitate its training process.
Initially, the model interprets raw data to find hidden patterns within the dataset. Subsequently, suitable unsupervised machine learning algorithms are applied based on the specific nature of the data.
Once the algorithm is applied, it divides the data objects into groups based on the similarities and differences discovered between the objects.
Types of Unsupervised Learning:
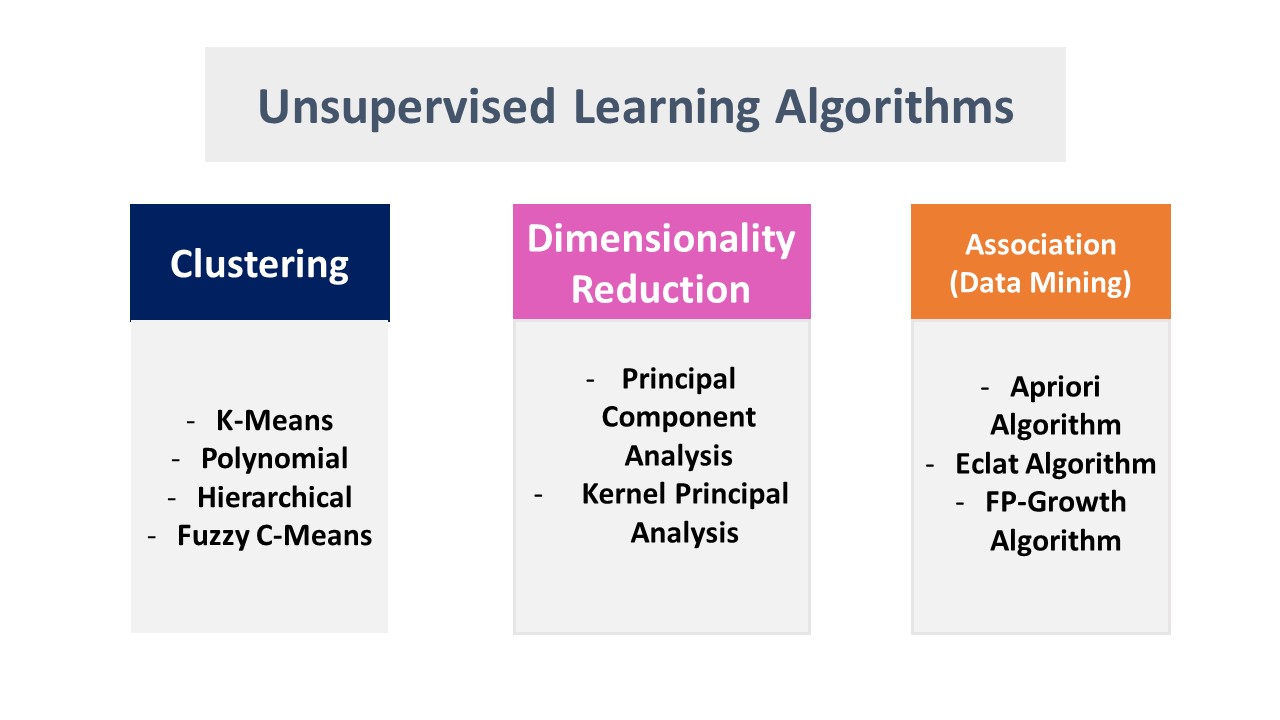 Unsupervised Learning Types and Algorithms
Unsupervised Learning Types and Algorithms
Clustering: Clustering is a method of unsupervised machine learning used to group objects based on their similarities.
Simply put, it categorizes objects into clusters by determining which data points share common traits.
Commonalities between data objects are identified through cluster analysis, and objects are then categorized based on the presence or absence of those similarities.
There are three primary clustering algorithms:
- K-Means
- Hierarchical Clustering
- Fuzzy C-Means
Dimensionality Reduction: Dimensionality Reduction (DR) is a method used to reduce the number of input variables in a dataset to make the processing smoother. These techniques can also be used alongside classification and regression datasets to create more efficient predictive models.
While there are many techniques within DR, the most well-known are:
- Linear Discriminant Analysis (often used in Supervised Learning)
- Principal Component Analysis (PCA - used in Unsupervised Learning)
Association:
An association rule is an unsupervised learning method used to discover relationships between variables in large databases. It determines sets of items that frequently occur together. Association rules make marketing strategies more effective—for example, identifying that people who buy "Item X" (e.g., bread) are also likely to purchase "Item Y" (e.g., butter or jam). A classic example of an association rule is Market Basket Analysis.
Why Use Unsupervised Machine Learning?
There are many reasons to use Unsupervised Machine Learning algorithms; here are some of the most compelling reasons for its use in various applications:
- USML helps us discover hidden insights within a dataset that might not be visible to the naked eye.
- Since it does not require labeled datasets, the model learns from its own experience, much like a human. This is a core component of true AI.
- In real-world scenarios, labeled datasets are not always available. Therefore, this method is essential for processing new, unstructured data.
Pros & Cons of Unsupervised Learning
Pros
- Unsupervised Machine Learning can handle more complex tasks compared to Supervised Learning. Because it works with unlabeled data, it is highly versatile.
- It is often preferable because unlabeled data is much easier and cheaper to obtain than manually labeled data.
Cons
- UML is intrinsically more difficult than supervised learning because it lacks predefined output values for validation.
- Usually, the degree of accuracy is lower than in supervised learning because the system does not know the exact output labels in advance.
Applications of Unsupervised Machine Learning
- Anomaly Detection: This identifies unusual data points in a dataset, which is vital for fraud detection.
- Recommender Systems: One of the most common applications, used by internet ventures such as Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Disney+, Amazon, Flipkart, Alibaba, YouTube, and Google Ads.
- Customer Segmentation: This allows businesses to identify target customers and present them with relevant products or services based on purchasing behavior.
- Genetics: DNA pattern recognition is used to identify genetic relationships and is a staple in medical research and development.
Powered by Froala Editor



