Introduction
Recently, we studied the two main types of supervised machine learning algorithms: regression and classification. Supervised machine learning utilizes a given set of input and output examples to help identify hidden relationships or data patterns. Since classification is a form of supervised machine learning, it also relies on these predefined datasets.
In this article, we will explore what classification algorithms are, their various types, different classification models, and the real-world applications of supervised machine learning.
What are classification algorithms?
Classification algorithms are supervised machine learning techniques that categorize datasets into various classes based on specific characteristics. Essentially, these algorithms perform the task of identifying which class an instance belongs to. In classification, the target variable is categorical. These algorithms are widely used in fraud detection, face recognition, and sentiment analysis.
What are the types of Classification Algorithms?
Mainly, there are two types of Classification Models:
- Linear Models
- Non-linear Models
Linear Models
There are two primary linear models:
- Logistic Regression
- Support Vector Machine (SVM)
Non-Linear Models
There are four main non-linear models in classification:
- K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN)
- Kernel SVM
- Naïve Bayes
- Decision Tree Algorithms
- Random Forest Classification
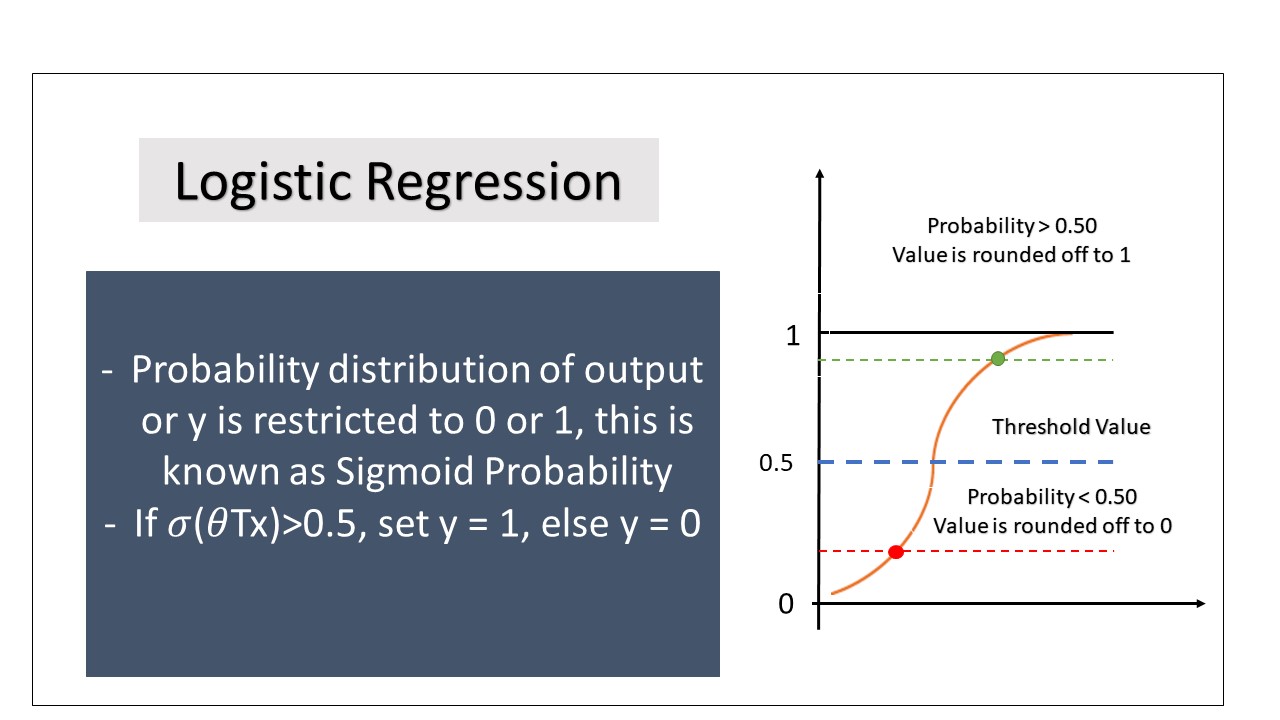
Logistic Regression: This model is used to predict binary outcomes for a given dataset of independent variables. It specifically handles binary results, such as 0 or 1, win or lose, day or night, pass or fail, and healthy or sick. Consequently, the output consists of discrete values where y belongs to the set {0,1}.
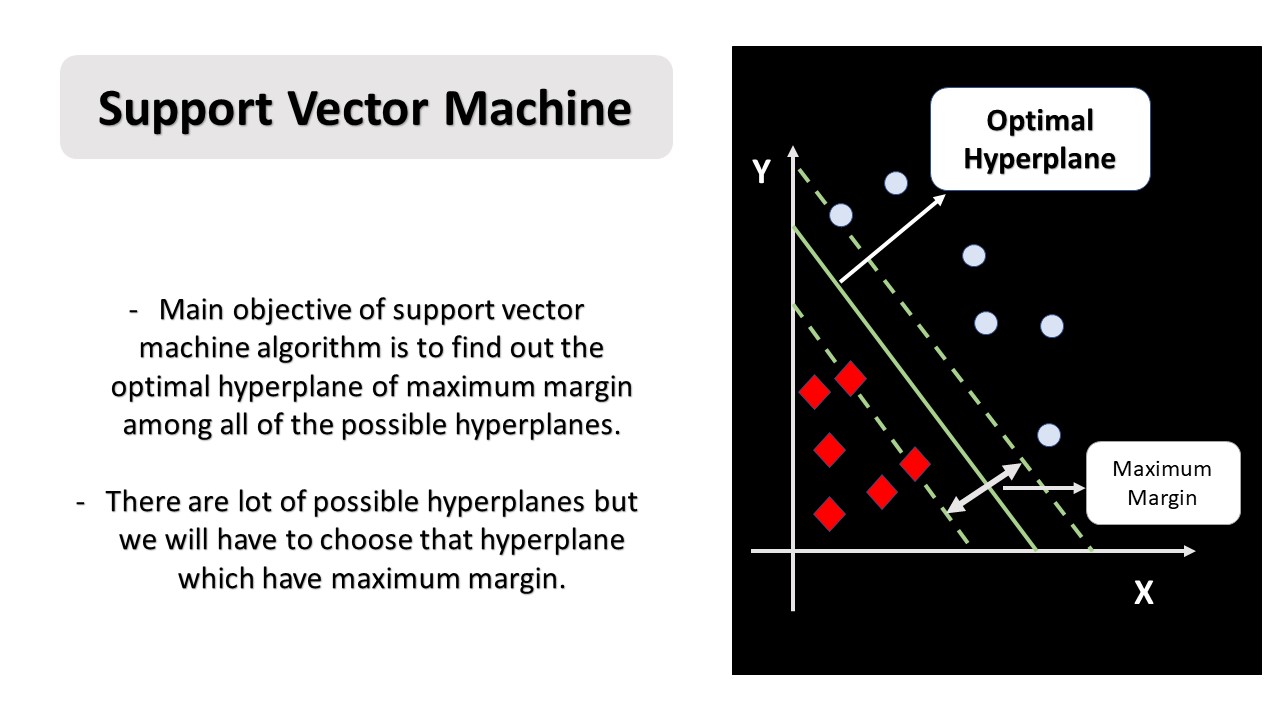
Support Vector Machine: The primary goal of a Support Vector Machine algorithm is to find a hyperplane in an N-dimensional space (where N is the number of features) that distinctly classifies the data points. While many possible hyperplanes can divide the dataset, our objective is to find the one with the maximum margin—the largest possible distance between the data points of the two classes.
K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN): KNN is a straightforward supervised machine learning algorithm that can be used for both classification and regression problems. It captures the concept of similarity (such as distance or proximity) using mathematical principles. It typically performs better with fewer dimensions; as the number of features increases, the system requires more labeled data to maintain accuracy.
Naïve Bayes: Naïve Bayes refers to classification techniques based on Bayes’ Theorem. Put simply, the Naïve Bayes algorithm assumes that the presence of a particular feature in a class is unrelated to the presence of any other feature. It is generally easy to build and particularly useful for large datasets. The algorithm typically follows three steps:
• Step 1: Convert the dataset into a frequency table.
• Step 2: Create a likelihood table by calculating the probabilities.
• Step 3: Calculate the posterior probability for each class using the Naïve Bayesian equation. 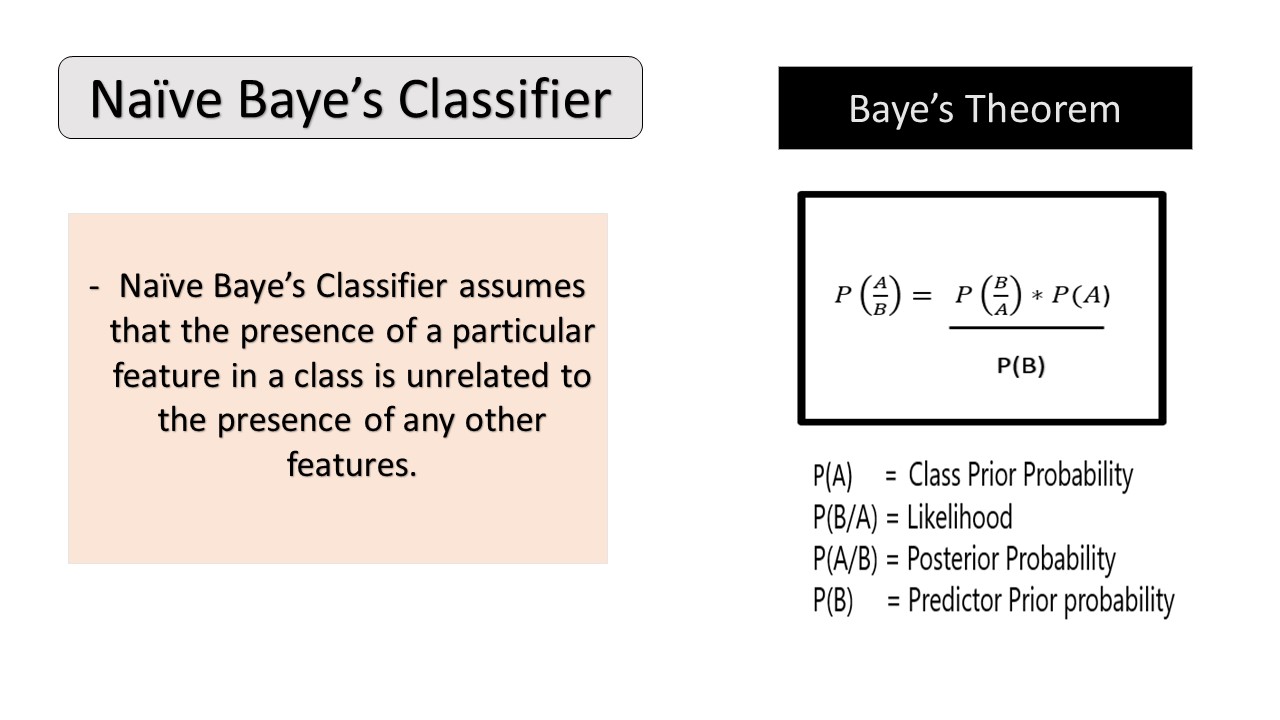
There are some common algorithms used for both regression and classification tasks.
Decision Trees algorithm: A decision tree is a flowchart-like structure consisting of internal nodes, branches, and leaf nodes. An internal node represents a feature (or attribute), a branch represents a decision rule, and each leaf node represents the outcome. The topmost node in the tree is known as the root node.

Applications of Classification Algorithms
Common applications of Classification Models include:
- Object Classification: Image classification algorithms are used to identify and categorize objects within digital images.
- Weather Forecasting: Weather prediction is a complex system involving many variables. While predicting a specific temperature is a regression problem, determining whether it will snow tomorrow is a classification problem.
- Customer Sentiment Analysis: Determining whether a customer is happy or unhappy is often performed via text analysis. These algorithms identify sentiments from feedback written by customers.
Powered by Froala Editor



