In layman’s language, cryptocurrencies can be understood using two words: cryptography and currency. Let’s understand both of these words one by one.
Cryptography: This is a technique that is used to protect information and communications through codes, so that only the sender (who is sending the information) and the receiver (who is receiving the information) are able to communicate.
Currency: Currency has its own uniform and unique history. From the era of the barter system to digital transactions (barter system, metallic coins, paper currencies, credit cards, and debit cards), the currency system has evolved over time. Currency is a medium of exchange for goods and services.
A cryptocurrency can be defined as a secure digital currency that uses cryptography and can be used online as a medium of exchange for goods and services. It can also be treated as a digital token.
Nowadays, many companies have launched their own cryptocurrencies, or they have adopted others, and these cryptocurrencies are traded within the respective companies as a medium of exchange for goods and services. Now let’s take a look at some wealthy and well-known individuals’ perspectives.
Some Negative Perspectives

This statement was given by one of the most famous and richest people in the world, Mr. Warren Buffett, on May 5, 2018. He is also the CEO of Berkshire Hathaway. But why did he make that statement?
According to him, cryptocurrency is just a buzzword, and people are buying it because they believe it will be used in the future. There is no real meaning in investing in it.

These are some negative perspectives. Now, let’s talk about the history and birth of Bitcoin.
History of Exchange and Cryptocurrencies:
- In ancient times, people used to exchange goods and services through the barter system. In the barter system, a person would give a certain quantity of goods or provide a service to another person, and the same would happen in return. However, trading within this system was very difficult because there was no common currency through which people could buy whatever they wanted.
- After centuries, people started trading using precious or simple metallic coins. These were regulated by monarchs or kings who ruled within dynasties. After the 16th century, paper currencies were introduced, and everything became centralized.
- Privatization, globalization, and liberalization were introduced in many countries. By the 19th century, a large number of cashless transactions were carried out using credit and debit cards.
Birth of Cryptocurrencies
- In the later decades of the 19th century, David Chaum introduced DigiCash, and Nick Szabo described Bit Gold.
- After the global financial crisis (in 2009 AD), Bitcoin was introduced by a pseudonymous user or developer named Satoshi Nakamoto.
Architecture
1. Blockchain Technology: Blockchain is an immutable ledger or data structure that holds transactions and tracks assets in a business network while ensuring transparency, security, distribution, and decentralization. An asset can be tangible (a house, car, cash, land) or intangible (intellectual property, patents, copyrights, branding). This can also be called the soul of the crypto system.
2. Digital Signature: It can be considered a digital version of an ordinary handwritten signature, but with higher levels of complexity and security. It can also be understood as a code that is attached to a message or document. After generation, the code acts as proof that the message has not been tampered with during its transmission from sender to receiver. There are two main components of a digital signature.
Hashing: Hashing is one of the core components of a digital signature. Hashing is performed using hash functions; these are functions that convert any size of input message into a fixed-size output. These functions are special algorithms such as SHA-256.
Cryptography: Cryptography is another component that is used in encryption and decryption methods. There are two types of cryptography:
- Symmetric Key Cryptography: An encryption system in which the sender and receiver of a message share a single common key that is used to encrypt and decrypt the message. The most popular symmetric-key system is the Data Encryption Standard (DES).
- Asymmetric Key Cryptography: Asymmetric key cryptography is also known as public key cryptography. It can be defined as an encryption process in which different keys are used for encrypting and decrypting information. The keys are different but mathematically related, making it feasible to retrieve plaintext by decrypting ciphertext.
3. Consensus Algorithm: As we have seen, blockchain architecture is cleverly designed, and each feature is linked with others. A consensus algorithm is used in the decision-making process for transactions among a group of active nodes on the network. When a large number of nodes participate in the validation process, an algorithm is required to make the process smooth. It works like a voting system, where majority nodes prevail over minority nodes. The consensus algorithm is what makes the entire blockchain system trustless.
There are several types of consensus algorithms, but the most common ones are:
- Proof of Work (PoW)
- Proof of Stake (PoS)
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
- Proof of Authority (PoA)
4. Mining: A miner’s goal is to add individual blocks to the blockchain by solving complex mathematical problems. This process requires enormous computational and electrical power. While many miners compete to add each block, the miner who solves the problem first adds the block—along with its approved transactions—to the blockchain.
Main Cryptocurrencies (Bitcoin & Altcoins)
1. Bitcoin: Bitcoin is the first decentralized cryptocurrency, created by a pseudonymous individual or team named Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009. It has been around for about 12 years, and Bitcoin has become the most well-known and valuable cryptocurrency.
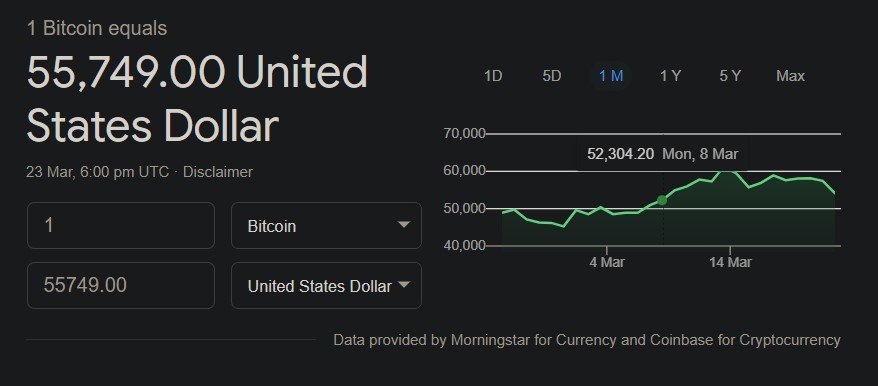
In 2021 AD, its value reached around USD 56k (as of March 2021). Traders can either purchase Bitcoin through exchanges or speculate on its price movements via CFDs.
Altcoins:
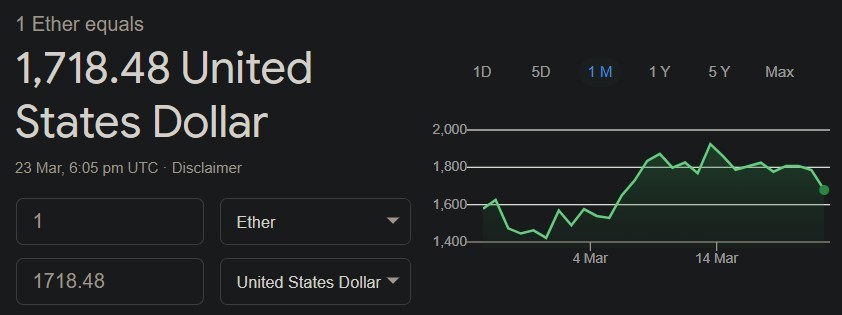
2. Ethereum: Ethereum is relatively new in the cryptocurrency world and was launched in 2015. It works in a similar way to the Bitcoin network. Ethereum tokens are known as Ether. Instead of focusing mainly on payments, Ethereum primarily supports smart contracts. A smart contract is a computer program or transaction protocol intended to automatically execute, control, or document legally relevant events and actions according to the terms of a contract or agreement.
3. Bitcoin Cash: Bitcoin Cash is a cryptocurrency and payment network created as a hard fork of Bitcoin in December 2017. A hard fork occurs due to disagreements between different communities or perspectives, usually regarding improvements to the software used within the network.
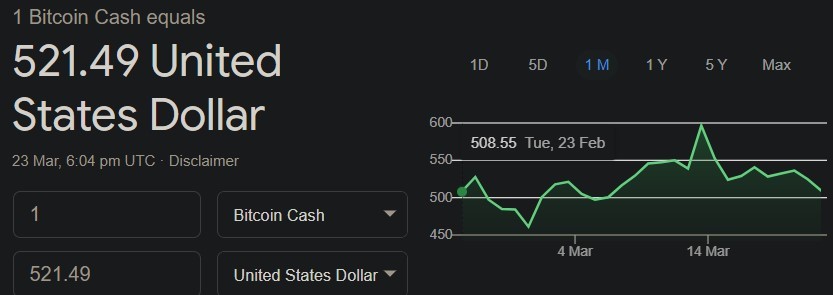
Bitcoin Cash can process transactions more quickly than the Bitcoin network, meaning shorter wait times and generally lower transaction processing fees. It can handle many more transactions compared to the Bitcoin network.
4. Litecoin: Litecoin is also one of the well-known cryptocurrencies. Charlie Lee studied the Bitcoin network and observed two major issues: slow transaction speeds and high costs. As a result, he decided to create a faster and cheaper cryptocurrency. On November 7, 2011, Bitcoin split into two, and the hard fork created a new coin called Litecoin.
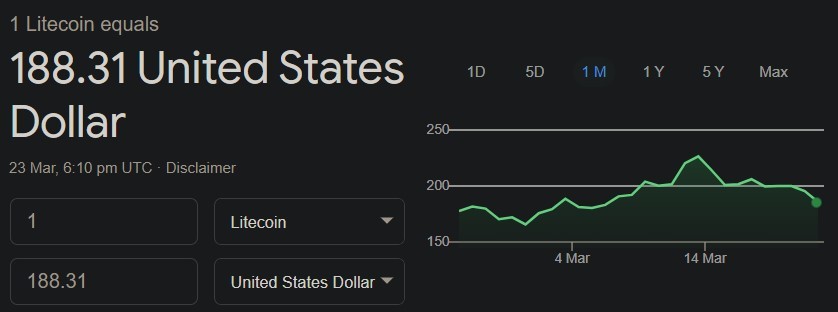
Litecoin takes less time compared to Bitcoin. Bitcoin takes approximately four times longer to process transactions.
Powered by Froala Editor



