Introduction
In 1959, Arthur Samuel defined machine learning as the field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed. However, this definition is considered informal.
Tom Mitchell later provided a more refined definition of machine learning:
"A computer program is said to learn from experience E with respect to some class of tasks T and performance measure P, if its performance at tasks in T, as measured by P, improves with experience E."
- Tom Mitchell
What is Machine Learning?
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence in which computers analyze data, identify hidden patterns or relationships, and extract information to provide meaningful insights.
For humans, it is very difficult to write complex programmed algorithms. However, through machine learning, computers or devices learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed.
It has various applications such as image processing, data mining, healthcare, video games, robotics, finance, and text analysis.
How does Machine Learning work?
Usually, whenever someone introduces machine learning, this question naturally arises.
A machine learning system identifies hidden patterns from historical datasets, builds predictive models, and produces output values from input values.
Let us understand each step one by one.
A machine learning system finds hidden data patterns or relationships between dependent and independent variables from multiple historical datasets of different data types and formats, including big data such as audio, video, and images.
Here, data types include continuous numerical, discrete numerical, categorical, and ordinal data.
After learning from historical datasets, machine learning builds predictive or forecasting models.
When unknown data points are introduced into these models, they generate outputs based on the learned relationships between input and output variables.
Types of Machine Learning
Machine learning can be categorized into different types based on the nature of learning, as follows:
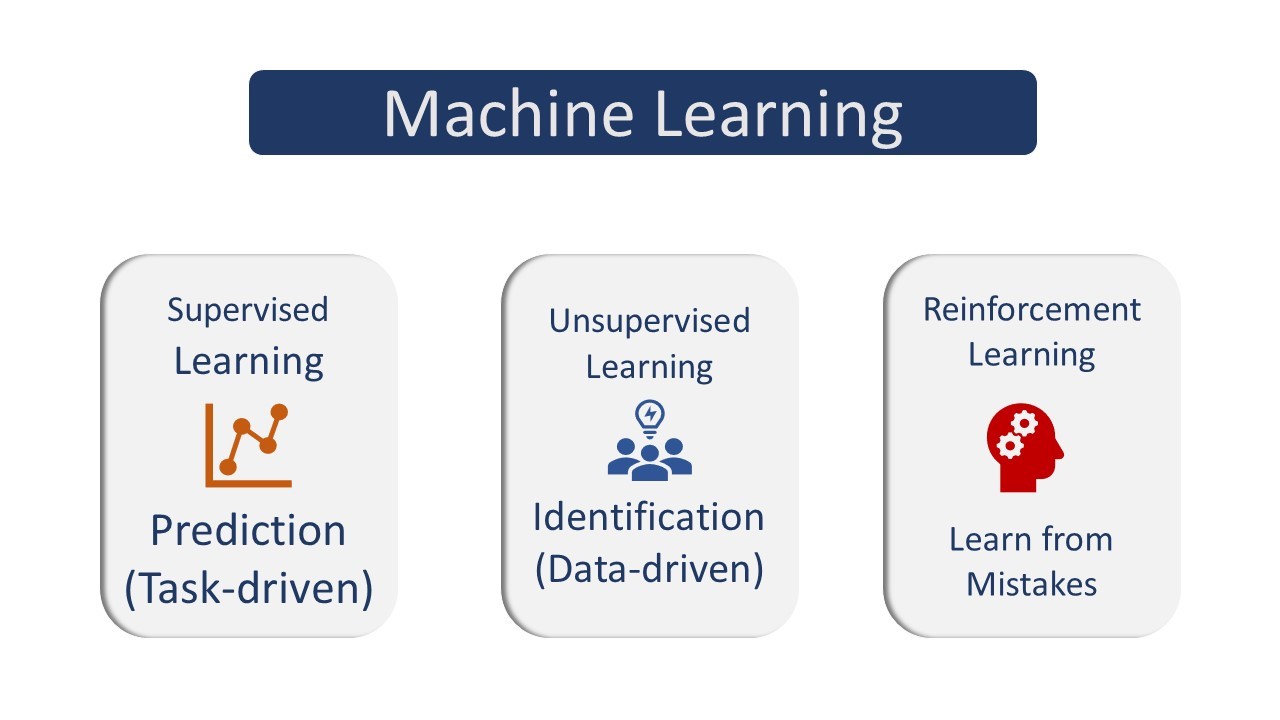
Supervised Learning
Supervised learning provides a powerful tool to classify and process data using machine learning techniques.
In supervised learning, labeled data (datasets with features and labels) are used to train algorithms that predict the classification of new, unlabeled data.
It is the easiest machine learning paradigm to understand and the simplest to implement.
It can be classified into two subcategories.
Unsupervised Learning:
Unsupervised learning is another category of machine learning.
In this approach, machines work with unlabeled and unclassified datasets to train algorithms. The algorithms explore the data and attempt to identify hidden patterns or structures within it.
The role of the machine is to group unsorted data based on similarities, differences, and patterns without any prior training.
There are mainly three types of unsupervised learning.

Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning is a category of machine learning in which software agents take actions in an environment to maximize cumulative rewards and minimize penalties.
In simple terms, models learn from past mistakes, and the system attempts to improve its performance in subsequent iterations.
It is used in robotics, business, gaming, navigation, data processing, training systems, and aviation. Reinforcement learning has three main components:
- Agent
- Environment
- Action
There are many algorithms in reinforcement learning that are applied across different domains, such as Q-learning, Deep Q Networks, Policy Gradient methods, and Markov Decision Processes.
Semi-Supervised Learning
Semi-supervised learning is another type of machine learning that uses both labeled and unlabeled data.
In simple terms, semi-supervised machine learning is a hybrid approach that combines supervised and unsupervised learning, consisting of a small amount of labeled data and a large amount of unlabeled data.
It is often more useful than supervised learning alone because labeling datasets is time-consuming and expensive.
However, it may introduce the possibility of human or emotional bias. It can be applied to classification, regression, and prediction tasks.
Applications of Machine Learning
Machine learning has numerous applications across various industries, including the automobile industry, entertainment, digital products, information technology, finance, fintech, and healthcare.
Some real-life applications include:
- Automation in automobiles: Examples include Tesla, Google, and Apple, along with their advanced automotive technologies.
- Recommendation systems: Widely used in digital products and software such as Google Ads, Netflix, Amazon Prime, YouTube, and similar platforms.
- Email spam detection: Used in email services such as Gmail.
- Image recognition: Applied in cybersecurity services and investigative agencies.
- Trading applications: Used in stock, cryptocurrency, and forex trading platforms such as Zerodha and Upstox.
- Fraud detection: Used by financial services, insurance companies, and fintech organizations.
- Speech recognition: Used in services such as Google Voice.
- Language translation: Used in tools such as Google Translator.
Powered by Froala Editor



